As per worldmetrics.org, 82% of businesses have embraced a hybrid cloud strategy in 2024. What does this staggering number display? Businesses are rapidly understanding and experiencing the benefits of cloud migration. Business leaders want to adopt cloud migration due to the benefits, like an extra layer of security, flexibility, and scalability that come with it.
Besides the above benefits, migrating to the cloud also saves enterprises a lot of money! Another Worldmetrics report states that 55% of enterprises expect to save 31% of IT costs, all thanks to cloud migration. Today, businesses prefer a combination of private and public cloud environments to optimize their operations.
But what is the other side of the coin? The revolutionary journey of migration to the cloud presents its own set of challenges. These cloud migration challenges, if not mitigated promptly, can disrupt business processes, increase costs, and delay the transformation process.
There’s always a silver lining, though. Just like the many problems, there are ways of mitigating them. Keeping in mind the innumerable benefits of cloud migration, enterprises should not avoid it because of the limitations. Instead, read this blog to find some useful ways of mitigating the most common challenges that might come your way.
What is Cloud Migration & Types of Cloud Environment
In layman’s terms, cloud migration is the journey of moving your business’s workloads, applications, data, and online assets from on-premise infrastructure to a secure cloud environment. This allows your organization to take full advantage of the benefits of cloud migration, such as enhanced performance and security, cost efficiency, and scalability.
Before diving deeper into the benefits, let’s understand the types of cloud environments. Organizations must carefully consider the available options in terms of workload sensitivity, required protection, operational needs, compliance, and costs.
The types of cloud environments are:
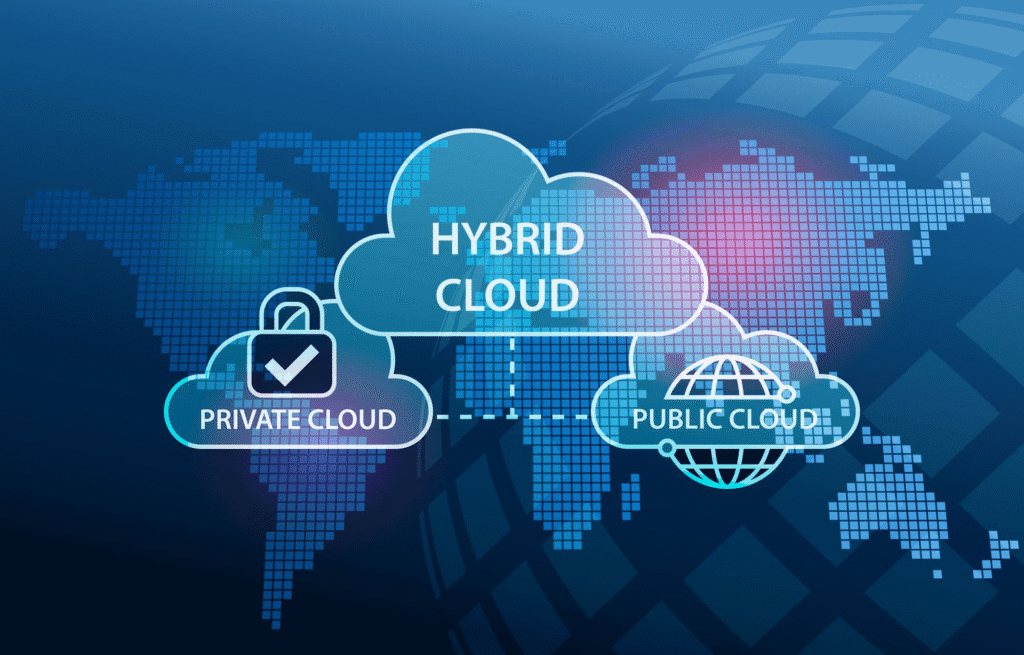
- Private Cloud: This refers to a cloud environment that is solely used by one organization. Though it is not as affordable as the other options, it provides comprehensive protection and control over compliance.
- Public Cloud: In the case of public cloud, third-party vendors like Microsoft Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud provide the services. This is a cost-effective option that offers scalability and flexibility, but can possess compliance and security issues.
- Hybrid Cloud: As the name suggests, it is a combination of on-premise and cloud environments that offer security, compliance, and cost efficiency. This is a top choice as hybrid cloud environments handle migration issues by allowing stepwise transition.
Benefits of Cloud Migration
Undeniably, more and more enterprises are making cloud migration a vital part of their digital transformation strategy. As per MARKETSANDMARKETS, the global cloud computing market is estimated to increase from $1294.9 billion in 2025 to $2281.1 billion in 2030 at a CAGR of 12.0% during this timeline.
These numbers clearly showcase the increasing importance of a cloud migration strategy in modern businesses for improved operations and revenues. Let’s quickly take a look at some of the exclusive benefits:
- Cloud environments match your business’s demand in real-time and let you scale resources accordingly.
- Cloud environments are mostly pay-as-you-go models, which omits the need for on-premise infrastructure and related costs, thus promoting financial savings.
- Cloud solutions provide flexibility to access data and applications from anywhere. This reduces operational interruptions in case someone can’t make it to work that day.
- With cloud migration, businesses get access to technological advancements like big data analytics and AI, which foster in-house innovation.
- SaaS development services like cloud migration provide robust disaster recovery to protect organizations against data loss and system failures.
- Due to the sustainable and energy-efficient nature of cloud data centers, migrating to the cloud also promotes a greener, cleaner, and more sustainable planet.
Top Cloud Migration Challenges With Solutions
1. Downtime & Business Issues

These are some of the common risks related to cloud migration. Downtime and business service problems can happen due to several reasons, including system incompatibilities, unpredictable technical glitches, data transfer problems, etc. In these cases, businesses need to have an effective mitigation strategy in place to avoid productivity and revenue loss, and other serious implications.
How To Mitigate?
- Generate a migration plan with properly defined times and stages.
- Test in a staging environment before conducting the actual cloud migration.
- Migrate in a phase-wise manner to decrease overall consequences.
- Try to migrate during idle hours to reduce productivity that can hamper business operations.
- In case of any unforeseen huge issues, always have a rollback plan in place.
- To make service available during the migration period, utilize redundant systems and load balancers.
2. Vendor Lock-In
It is one of the most commonly faced issues by businesses that become overtly dependent on one cloud provider’s proprietary services or technologies. With time, this dependency can cost you extra expenses, a lack of flexibility to change service providers, or move back to on-premise infrastructure.
How To Mitigate?
- From the initial stage, develop a portable cloud architecture.
- Utilize containerization technologies, such as Docker, to avoid cloud migration risks.
- Use a hybrid or multi-cloud strategy to disperse migration risks across various providers.
- Do not rely completely on proprietary services and understand the importance of open standards.
- Backup data regularly.
- Use cloud migration tools and platforms to reduce migration risks.
3. Data Security Problems
During the cloud migration process, data protection is of utmost importance. Sensitive information can be prone to data breaches, cyber attacks, and unapproved access. The risk is especially higher when the data is being moved around networks and stored at different locations in the migration journey. If a security breach occurs at this time, it can damage reputations, have legal consequences, and even cause severe financial losses.
How To Mitigate?
- You must have end-to-end encryption for moving and storing data.
- Using secure transfer protocols like HTTPS can reduce data breach chances.
- Before, in-between, and after migration, you must conduct extensive security audits.
- Apply strict access controls and multi-factor authentication.
- Collaborate with trusted cloud service providers who offer the best security standards and compliance certifications.
- Keep all systems and applications patched up and updated to reduce risks.
4. Data Loss

Data migration is a complicated process and has several risk factors attached to it, including data loss or corruption. This can take place in case of transfer or human error, and compatibility issues between systems. For enterprises managing sensitive or vital information, data loss issues can have massive repercussions.
How To Mitigate?
- Many software engineering firms offer trusted data consultation, and you can appoint one during the cloud migration process.
- Have a comprehensive and planned data backup and recovery system before initiating the migration.
- Use sample data for test migrations before commencing with the migration of your entire dataset.
- Data validation tools, like Google Cloud’s Data Validation Tool (DVT), are used to test the integrity and completeness of the migrated data.
- Have multiple copies of data.
- Implement data verification methods or checksums during the migration process.
- You must also use incremental data migration methods to minimize loss of data on a large scale.
Also Read: Top Open-Source Data Analytics Tools for Smarter Insights
5. Problems in Performance
After moving data to the cloud, some businesses might face degraded performance. This can be due to several factors, including resource contention in shared cloud, increased network latency, or not optimizing applications for cloud architecture. Issues in performance can affect businesses by decreasing productivity, offering a poor user experience, and even reducing customers and revenue.
How To Mitigate?
- Performance testing is a must before, after, and during the migration process.
- Factors like caching and stateless design can affect performance. To avoid these issues, optimize all applications for cloud environments.
- For geographically distributed users, utilize CDNs (Content Delivery Networks).
- To avoid performance-related problems, opt for the correct instance types and sizes for your workloads.
- To manage a sudden increase in traffic and sustain performance under load, use auto-scaling.
- You can also use managed database services to offload performance tuning and maintenance.
6. Compliance Violations
For industries in highly regulated industries, like finance, healthcare, government, etc., compliance violations can be costly. Compliance violation risks in cloud migration increase when data is stored in geographically different places or if a third-party cloud service is used. Several locations have strict data protection laws, such as HIPAA and GDPR, to evaluate compliance, violation of which can lead to huge fines and legal actions.
How To Mitigate?
- Assess the risks of data migration by conducting risk assessments with a focus on compliance.
- Opt for cloud service providers who provide compliance-specific solutions and certifications.
- Apply data residency controls to make sure that all the data is stored in compliant places.
- Audit the compliance of your cloud environment on a regular basis.
- Manage sensitive data with utmost precision using data classification tools.
- For compliance reporting, maintain logs and documentation in detail.
7. Cost Overruns
Cost overruns, if not well-managed, can rapidly reduce the financial benefits of cloud migration. It can be caused by an improper understanding of resource requirements, not knowing cloud pricing models, and not optimizing cloud usage.
How To Mitigate?
- Carry out a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis.
- Before migration, evaluate the pricing models of your opted cloud service provider.
- To monitor and optimize expenditures, use cloud cost management tools.
- Review cloud usage daily and align resources accordingly.
- If reserved instances or committed use discounts for predictable workloads are available, use them to your advantage.
8. IT Team Skill Gap
The skill set required for cloud migration is different from that of traditional on-premise infrastructure. Various cloud migration risks can occur, like suboptimal configurations, inefficient resources, and security issues, in case your IT team does not have the required expertise. This can lead to an incapacity to leverage cloud benefits and a decrease in efficiency of the entire migration process.
How To Mitigate?
- Thoroughly check your IT team’s capabilities by conducting a skill assessment.
- Arrange for robust cloud training and certification programs for upskilling your employees.
- You can also appoint a cloud consulting service or cloud specialists to work closely with your staff.
- Create a knowledge transfer plan to spread cloud expertise within the IT team.
- Develop a Cloud Center of Excellence (CCoE) to educate employees on cloud migration, best practices, and risks.
- Ensure your IT team is updated on the latest cloud developments and regulations.
Also Read: Top Cybersecurity Careers in 2026
9. Incomplete/ Incorrect Data Migration
Incomplete or inaccurate data migration is another risk factor associated with cloud migration. It can be caused due to factors, like incompatibilities between source and target systems, issues with data formatting, or missing datasets completely.
How To Mitigate?
- Create a migration plan that incorporates details of all data sources and types.
- Opt for a comprehensive data cleansing and audit before the migration process.
- Utilize data migration tools with in-built validation checks.
- Use a staged data migration approach, initiating with non-essential data.
- Migrated data should be robustly checked and validated.
- For auditing and troubleshooting, maintain detailed logs.
- If any vital issues are detected in the data post-migration, create a roll-back plan beforehand.
10. Challenges with Integration
When integration takes place between cloud-based systems and on-premise applications, you might face several challenges. These integration challenges can lead to data silos, issues with workflow, increased cost and time of project migration, and productivity inefficiencies.
How To Mitigate?
- Assess your latest IT infrastructure and integration requirements.
- Create an integration strategy as a significant part of your entire migration plan.
- Utilize iPaaS solutions or cloud integration services.
- Leverage API management tools to efficiently integrate between different systems.
- Approach integration in phases, starting with vital systems.
- Before making live, comprehensively test integrations in a staged environment.
- Maintain all integration documents and a centralized integration architecture.
Cloud migration challenges can be risky for organizations in all industries, especially in the sensitive ones. On the brighter side, this transformative process has huge benefits that outweigh these challenges in comparison. Having an elaborate cloud migration strategy will not only reduce migration-related risks but will also ensure a seamless integration.
The evolving digital scenario requires businesses to adapt to technological innovations like cloud migration for greater security, scalability, and productivity. By changing the way your business operates and stores data using cloud migration, you can achieve the pinnacle of success in negligible time.
Also Read: Top 5 Frameworks for Deep Learning in 2025







