Imagine using one computer as if it were multiple in number. Yes, you can with virtualization techniques in cloud computing. Before the introduction of virtualization, one computer could manage one job at a time. This led to the wastage of their power and inefficient workload distribution. The primary purpose of virtualization is to enable the simultaneous operation of multiple virtual computers on a single physical computer. This enables you to accomplish more tasks and utilize the full potential of your computer.
In virtualization in cloud computing, the above idea is taken one step further. Cloud service providers split one huge server into smaller virtual servers using virtualization. With this, organizations can utilize only what they need, without incurring any additional costs or hardware expenses.
In this blog, I will take you through the technical definition of virtualization, its types with examples, and the advantages and disadvantages of virtualization in cloud computing.
What is Virtualization in Cloud Computing?
Virtualization is when several virtual resources, like applications, servers, and storage, run seamlessly on one physical machine. It also allows the accommodation of multiple users at a time.
Without virtualization, one physical machine will be needed for each user, which will add to inefficiencies and costs. Virtualization creates separate virtual entities for individual users on one physical machine and helps to optimize the utilization of resources.
Virtualization enables saving energy through workload and server consolidation. In the case of overloaded servers, virtual machines (VMs) can be transferred to underloaded ones. And underloaded servers can consolidate VMs, which allows idle servers to be turned off.
Some relevant terms that you need to know when discussing virtualization in cloud computing:
- The physical machine that accommodates the virtual machines is called the host machine.
- The virtual machine operating on the host machine is called the guest machine.
How Virtualization Works?
Virtual uses a single physical computer to work. On that physical computer, it runs multiple virtual machines at one time using a software program, a hypervisor, more on it soon. Each VM operates like a standalone computer using the same physical machine.
Some vital pointers to keep in mind:
- Once the virtual software is installed, users can create one or more virtual machines on their computer.
- VMs behave exactly like regular applications on the user’s system.
- One host can operate multiple guest virtual machines.
- Every guest has their own operating system, which may or may not be different from or the same as the host operating system.
- Each VM functions like an isolated computer, having its own programs, configurations, and settings.
- VMs use system resources, like RAM, CPU, etc., but work in a way as if they are using their own hardware.
Hypervisor in Cloud Computing
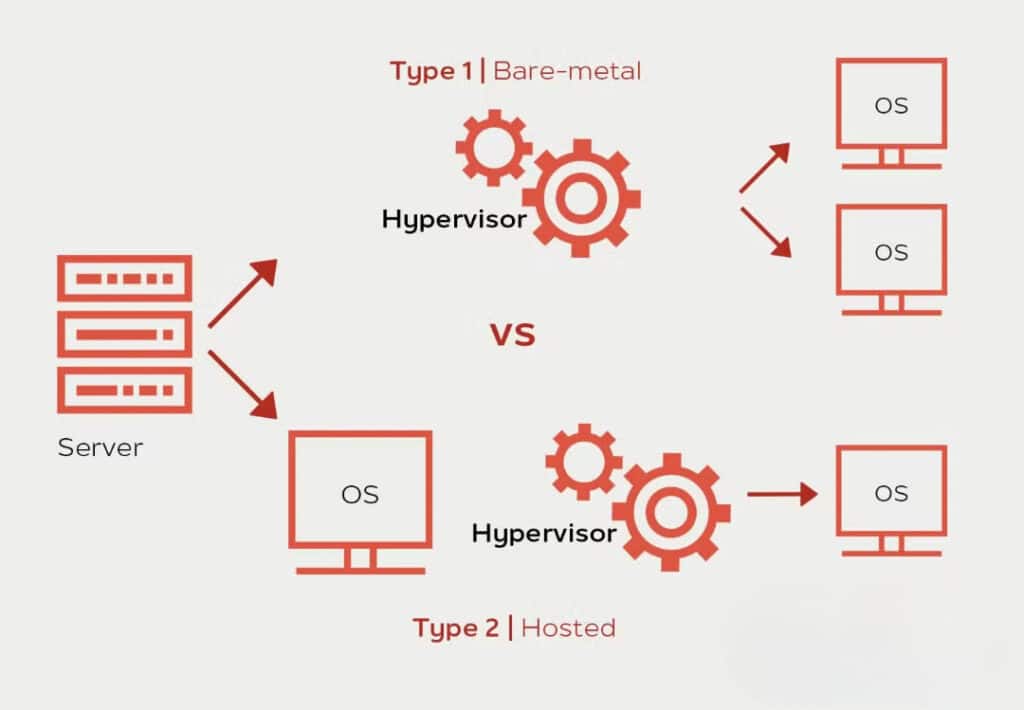
A hypervisor is a software that is the backbone of virtualization. It acts as an intermediary between the physical computer and the VMs. It manages and splits the resources of the host machine, like CPU, storage, among the various virtual machines.
Hypervisors can be of two main types:
- Bare-Metal Hypervisor (Type 1) – This type is a highly efficient one, as it has direct access to all the resources of the computer. It can be directly installed on the computer’s hardware, eliminating the need for an operating system.
- Hosted Hypervisor (Type 2) – This type is utilized when users need to execute multiple operating systems on one machine. It runs on top of any existing operating system, like macOS or Windows.
Also Read: Migrating to the Cloud: Top 10 Data Migration Challenges and Solutions
Cloud Virtualization Types & Examples
1. Server Virtualization
Using a hypervisor, server virtualization separates a physical server into several virtual servers. This allows better scalability and resource utilization since each virtual server operates on its own applications and OS.
Example of Server Virtualization
An organization has a potent physical server, and it can use server virtualization software, like KVM, Microsoft Hyper-V, and others, to generate multiple virtual machines on that single server.
Benefits of Server Virtualization
- Each server can be restarted separately without impacting the operation of other virtual servers.
- With server virtualization, one server is divided into different virtual private servers. This reduces hardware cost.
- Disaster recovery is simple with server virtualization, as data can be stored and retrieved from any location. It can also be transferred from one server to another quickly.
- With server virtualization, you can keep private information in data centers.
2. Network Virtualization
Network virtualization makes virtual versions of network resources, such as switches, firewalls, etc. It enables improved network management and isolation. The important features are network isolation, logical network creation, and software-defined networking (SDN).
Example of Network Virtualization
One of the examples is Google Cloud. By using Google Cloud, organizations can generate their own networks using software without the need for physical devices. Things like IP addresses, private connections, and firewalls can be easily set up in the cloud. This way, organizations can manage, scale, and change their network without any hardware requirements.
Benefits of Network Virtualization
- Enhances network management.
- Reduces the need to set up different physical networks for different node groups.
- Improves the utilization of network resources.
- Improves the performance of virtual machines.
- Increases security by isolating sensitive data from one VM to another. Also, node accessibility is restricted in a VM from another VM.
3. Desktop Virtualization
With desktop virtualization, users can use their desktop environment remotely hosted on a centralized server. You can generate various virtual desktops that can be used from any device, like tablets, laptops, etc. It offers flexibility, portability, and facilitates software updates.
Example of Desktop Virtualization
Edtech companies can utilize services like Google Cloud (GCP), Virtual Desktops, or Amazon Workspaces to provide access to their team members to the same coding setup and tools they require to access team work. With this, team members can log in from any device and use a virtual desktop that runs well in the cloud.
Benefits of Desktop Virtualization
- Improved data security.
- Decreased costs on hardware.
- Easy management and updation, making it highly utilized in remote work, educational institutions, etc.
4. Storage Virtualization
With storage virtualization, organizations can abstract multiple physical storage resources into one virtual system. This enables better resource management and utilization. In case of an underlying hardware failure or change, storage virtualization ensures seamless performance and operations.
Example of Storage Virtualization
Amazon S3, a type of storage virtualization, can store data from anywhere and in any quantity. When an organization has innumerable files and data to store, it can use Amazon S3 to store them securely, without any issues, and also provide access from anywhere.
Benefits of Storage Virtualization
- Storage virtualization offers centralized management.
- Users can alter their storage capacity whenever required.
- Allows organizations to seamlessly manage a large amount of data and files without the need for any supplementary physical storage hardware.
- Data backing up, recycling, and disposing becomes very simple and quick.
- Promotes optimized resource usage, enhances data access, and saves money.
5. Application Virtualization
With application virtualization, users can operate applications using virtual containers without installing them on the operating system. It provides users with remote access to directly interact with deployed applications. The data and application settings are saved on the server, but users can run it locally using the internet.
Example of Application Virtualization
One popular example of application virtualization is Microsoft Azure. It allows people to use applications without installing them on their devices first. Users can access applications from their desktops or laptops once the application is established in the cloud. These applications run on Azure’s server, so it makes working faster, smarter, and efficient.
Benefits of Application Virtualization
- Reduces compatibility issues, hardware, and software costs.
- The IT team can centrally manage, deploy, and patch applications. There is no need to manually install or update applications across several devices.
- There is a decreased chance of security breaches and malware since the applications are separated within virtual environments.
- Offers flexibility as users can access applications from anywhere or any device.
- Reduced chances of local device crashes or slowdowns due to software issues as applications run on host servers.
6. Data Virtualization
With data virtualization, users can get a merged view of data from multiple sources, as it accesses and integrates this data without moving or copying it. This unified view of the data can be accessed remotely via cloud services.
Example of Data Virtualization
Oracle, IBM, TIBCO, CData, and other tech companies offer data virtualization solutions.
Benefits of Data Virtualization
- Provide real-time access to data from multiple sources.
- Eliminates the requirement of expensive ETL processes, duplicate storage, and extra infrastructure, cutting expenses.
- Simplifies data management by offering centralized access and security management.
- Swift adaptation to transforming regulatory and business requirements.
- Provides relevant users with concurrent access to unified and governed data, offering quicker and more collaborative analytics.
Also Read: RPA in Business: A 2025 Guide to Working Smarter, Not Harder
Advantages & Disadvantages of Virtualization in Cloud Computing

Till now, we have understood together what virtualization is, its types, examples, and other aspects. But one of the most notable aspects of virtualization is the benefits it offers. As with any other technology, there are also some limitations of virtualization in cloud computing. Before discussing the cons, let’s take a look at the benefits.
Advantages of Virtualization:
- With virtual, both the user and the cloud service provider can utilize hardware efficiently.
- Virtualization offers advanced features that allow the availability of virtual instances all the time.
- Virtualization makes real-time data recovery, duplication, and backup simple.
- Virtualization aids in saving energy as it reduces the monthly power and cooling costs when transferring from physical to virtual servers (the number of servers decreases).
- The entire process of virtualization setup is less time-consuming than traditional setup, and even quicker and simpler.
- With virtualization, cloud migration becomes an easy task. Since the data is already on the server, it can be quickly and securely transferred to the cloud server. This saves time, cost, maintenance charges, and power consumption.
- It allows efficient resource utilization of physical hardware as it operates several virtual machines on one physical server.
Disadvantages of Virtualization:
- When compared to a traditional setup, the initial cost of storage and servers can be quite expensive.
- Virtualized environments can be complicated to manage, especially with the rising number of virtual machines (VMs).
- When not monitored and configured well, virtualization’s additional layers can have security risks.
- Companies that have a skilled team to handle cloud environments or have the budget to upskill existing employees or hire new ones should incorporate virtualization.
- With virtualization, data is hosted on third-party resources. This can pose data security issues as hackers can attack the data or gain unauthorized access.
Today, virtualization is an important technique in cloud computing. It efficiently utilizes physical resources by generating several virtual instances. Virtualization offers numerous benefits, like cost-cutting, flexibility, operational efficiency, and many more. This makes it a vital part of the latest cloud computing. Its primary applications in data management, cloud computing, and business intelligence (BI) make it an inseparable part of modern organizations globally.







