Do you ever marvel at how businesses and governments seem to know what their people need even before the trend begins? How are they prepared to handle risks like economic, environmental, or social, long before they take place? This isn’t magic, it’s something called strategic intelligence.
For instance, imagine a clothing brand, X, keeps on being well versed with the ongoing trends, cultural shifts, the market data, economic alterations in the apparel industry, people’s shopping habits, the social media buzz in dressing sense, and global reports. With such a great set of data and information, brand X can easily comprehend what people will love to buy next season. And while their competitors will still be in the guessing game, brand X has already stacked their shelves with the demanding designs. That’s how strategic intelligence can change simple information into doable steps.
The world is time-sensitive now, and the stakes are higher than ever. There is no lack of information. The World Economic Forum’s strategic intelligence platform scans over 1,000 publications on a daily basis from almost 250+ organizations and brain trusts to figure out emerging risks and work towards their mitigation. This truly exemplifies the importance of the information needed to stay ahead.
Aren’t you excited to know more about what is strategic intelligence, and how it has come a long way from the Cold War to tech and business? Let’s deep dive into it and understand everything about this much-needed intelligence system.
Strategic Intelligence: Definition & How it Began?
Strategic intelligence is a process of gathering information and thoroughly analyzing it to convert it into a roadmap for long-term decision-making. In simple words, it’s not about solving present problems but gearing up for the upcoming challenges or disasters in the future, and also determining future opportunities.
World War II is one of the greatest strategic intelligence examples, that how intelligence turned out to be a boon for the Allies as they gathered intelligence on weather reports, German defense systems, and deception campaigns, which helped them to make a strategic plan to fight the Nazis. The outcome was a win for the Allies with a successful Normandy invasion, the largest invasion in history, operated on land and water, and a decisive stage in the war.
Today, the same approach and tactics are used outside warfare, which helps businesses and governments to predict risks and mitigate them.
How Strategic Intelligence Came into Play?
The idea of strategic intelligence mainly came into place for the need of military and national security, as it traces back to the history of wars. Winning in battlefields was just not about fighting with weapons but brains too, and it required the understanding of the bigger picture to get an idea of the bigger threats and opportunities.
The term came into existence with WWII & the Cold War, where countries like the U.S. and U.K. developed systems to collect and study information from various sources. And over time, this idea of future-predicting techniques started to be used in business domains.
Related: What Is Paid Search Intelligence? Know All About It
How Strategic Intelligence Works?
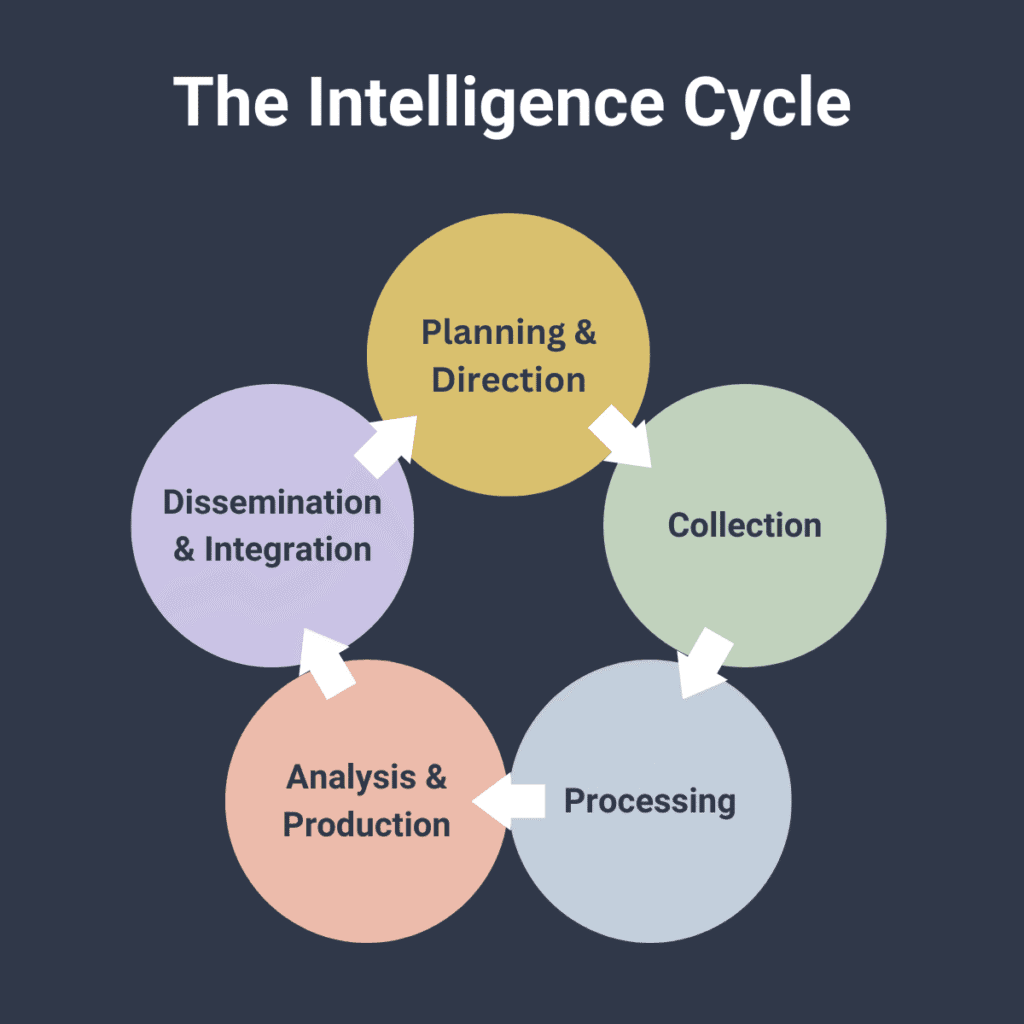
There are several steps involved in proceeding with effective strategic intelligence.
1. Planning
First, decide the set of questions that needs to be answered and identify problems to be solved. This creates a framework for intelligence to work in a focused manner. Example: The Government may ask ‘Is there any probability of cyber threats?’, and the intelligence will work accordingly.
2. Data Collection
Gather information from various sources, such as open sources, human sources, and technical sources, and focus on gaining as much relevant information as possible, avoiding skewed or fluff data.
3. Processing & Sorting
Collected information is modified into a simple and easy-to-understand form, and the best possible plans are made using it. This step includes translating documents, arranging numbers, or mapping patterns for easy strategic intelligence analysis.
4. Analysis and Interpretation
Here, the information is studied to find trends, organizing patterns, and any important connections. This gives an understanding of what the data is really trying to address.
5. Visioning
After analysis comes a stage to future-gaze what might happen, is there any advantage, or an upcoming mishap? For businesses, it can be predicting marketing trends, and for defense, it can be gauging enemy moves.
6. Dissemination
The compiled insights are shared with the right set of people who can make a plan for the correct measures to be taken. They are provided with reports, briefings, or dashboards. On-time information is key in decision-making.
7. Decision-Making
Leaders use the shared information to take effective actions. Companies design product launches, governments make policies, and the military carries out operations and strategies on the basis of this processed information.
8. Feedback & Updating
After the action plan is executed, there is a new set of information and data, which is fed back into the process. This is done to keep intelligence updated and adaptable to changes.
Related: What’s the Importance of Analytical Intelligence in Today’s Workplace?
Types of Strategic Intelligence
| Type | What It Focuses On | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Military/ Defense | National security, enemy capabilities, and battlefield planning | WW II Allied forces studied German troop movements before D-Day |
| Economic/ Financial | Markets, trade trends, and financial risks | Inflation, global money policies, and competition tracking |
| Political/ Diplomatic | Policies, stability, and intentions of countries or political groups | Monitoring global elections or international treaties |
| Business/ Competitive | Market trends, competitors, customer needs | Tech company analyzing competitor product launches |
| Technological/ Scientific | Innovations, R&D trends, new technologies | Tracking AI or renewable energy opportunities |
| Social / Cultural | Societal vogue, human behavior, cultural shifts | Studying changing demands and needs of consumers, or social movements |
Strategic Intelligence Platforms
These platforms are tools, generally software, helping organizations in data collection, organization, and analysis of large sets of information in one place. Traditional sources can not handle multiple sources at once with real-time updates, but these strategic intelligence platforms support this to give insights and ensure smooth team collaborations.

How Does it Help?
- Support faster decisions by real-time updates, allowing leaders to act quickly.
- Better long-term planning with forecasting and future scenario study.
- Streamlines the processes as the same data is smoothly fused across teams and departments, or countries, for effective collaboration and communication.
- Early warnings keep organizations and nations alert for risk management.
Examples of Strategic Intelligence Platform
- Quantive’s Strategic Intelligence Platform
Businesses can keep track of market trends, competitor performances, and global happenings in their industry and related fields.
- World Economic Forum
Over 1000 publications are processed daily, through which leaders can track global risks, trends, and advantages to make informed decisions.
- Palantir Foundry
Brings together a large number of datasets, which governments and businesses can turn complex information into usable insights for planning and executing.
Some Widely Used Sources for Strategic Intelligence
| Intelligence Type | Primary Uses | Countries |
| Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) | To go through publicly available information (news, social media, reports) for understanding. | USA, UK, Israel, China, India, France, Germany, Russia. |
| Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT) | Satellite imagery is used, and information is laid out for military planning, disaster response, and watching over the environment. | USA, UK, Israel, India, France, Germany, Russia, China. |
| Human Intelligence (HUMINT) | Gathering information from human sources through espionage, interviews, and debriefings. | USA, UK, Israel, India, France, Germany, Russia, China. |
| Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT) | Pointing out and examining physical phenomena (e.g., chemical, nuclear, or electromagnetic signatures) to pin down threats. | USA, UK, Israel, France, Germany, Russia, China. |
| Signals Intelligence (SIGINT) | Intercepting electronic communications and signals to gather intelligence. | USA, UK, Israel, India, France, Germany, Russia, China. |
Related: Top 5 Market Intelligence Platforms for B2B Success
Benefits of Strategic Intelligence
Understanding and leveraging strategic intelligence can be of utmost advantage to organizations. It’s just amazing that you can use some simple gathered information, and it can lead to winning even wars. There are various benefits of implementing intelligence in your work practices.
- Improved decision-making
- Early threat detection
- Over the edge advantage
- Making the most of resources
- Beneficial for long-term planning
- Risk management
- Reduces response time, ie, faster response
- Nurtures breakthrough thinking
Conclusion
Strategic intelligence isn’t just any fancy idea; it’s a serious job, and it comes with impactful measures. A recent study suggests that 236 leaders in Jordan experienced a remarkably faster performance and more firm decision-making by using BI (Business Intelligence). Commercial banks in Kenya saw better returns and strong positioning among competitors by opting for strategic intelligence services.
So if you’re running a business or handling a nation, making use of strategic intelligence is always worth it. Along the way to victory, you will experience fewer unexpected challenges, a reduced amount of threats or vulnerabilities, and clearer paths and advantages over those who are not leveraging this intelligent system.