The emerging and fascinating field of computer science is quantum computing, the foundation of which is quantum mechanics. Engineering is pushing the boundaries of imagination to develop this technology, and soon it will be able to solve problems that classical supercomputers can’t solve exponentially faster or at all.
In this article, I will take you through the mechanics, the advantages, and the disadvantages of quantum computing.
Introduction to Quantum Computing
Classical computing, the one powering your laptop and smartphones, is built on bits (storing data as either 0 or 1). But in contrast, quantum computing is built on qubits that are capable of storing information in multiple states simultaneously, i.e., it can store both 0 and 1 at once. Classical computing uses binary logic, which means it processes information as 0 or 1, solves problems, at one particular state at a time. Whereas quantum computing uses parallel logic, which enables computers to process information as both 0 and 1 in multiple states at the same time to solve much more complex and time-consuming problems quickly.
Core Principles of Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanisms and especially the phenomena behind them often leave people in awe. It is obvious, though, because it involves experiments and findings that show a completely different behavior of the universe than in our normal life. These findings often spark counter-debates, and the curiosity of finding the why never ends.
To understand the crux of quantum computing, it is important to understand these four key bases of it:
Superposition
Qubits hold the state of superposition, which means they represent information as 0 or 1 at the same time. And group of qubits can make a complex multidimensional computational space, and processors can figure out many possible solutions simultaneously.
Entanglement
This element has an unexplained why behind it, because entanglement means a type of correlation or synchronisation between qubits where the change in one qubit affects the other. They follow a shared rule, whether anti-relation or correlation or any other, depending upon the quantum circuit.
The reason behind entanglement is not discovered, though it is said to be the fundamental property of quantum mechanics.
This principle allows qubits to have exponential storage power; 2 qubits can store and process four bits of information, 3 qubits can handle 8, and so on. This scaling power gives quantum computers an edge over classical computers.
Interference
It is an environment where two quantum states combine. Here, qubits behave like waves to interact with each other. Either they will combine in a positive manner, where they will sync, or in a negative manner, where they will cancel each other. Sometimes, the wrong and right solutions exist in parallel. And this interference in quantum algorithms enhances the probability of the correct solution while eliminating the wrong ones by cancelling their probability waves.
Decoherence
It is actually not a principle but a bad omen to quantum mechanics, a process where the qubits lose their quantum properties due to external interference. It can happen intentionally while measuring a quantum system or can be triggered by environmental factors like temperature, noise, electromagnetic signals, and more. Here, leaving their quantum abilities, qubits break down into a classical state (only processing 0 or 1 at once).
Working of Quantum Computing
They work on two bizarre, yet true ideas. One is that any object can be in definite states, i.e., qubits in superimposition behaving randomly, and the second is that no matter the distance, these objects will correlate and respond to each other, that is, the entangled qubits. They are individually random yet connected.
The qubits are put into a superimposition of computational state, then using quantum circuits qubits entangle and generate interference patterns ruled by quantum algorithms. Numerous possible outcomes are cancelled out (destructive interference), and others are amplified (constructive interference). The amplified outcomes are the solutions to the handled problem.
Related: Important Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Major Quantum Computing Technologies
Currently, there are five-qubit technologies being explored by organizations and their efforts to develop a beneficial quantum computer for all. These technologies are:
- Superconducting qubits
- Trapped ions
- Photonic qubits
- Spin qubits
- Neutral atoms
Some of the other explored technologies include topological qubits and NV-center qubits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantum Computing
Every technology can serve you as a boon or make you a bait; let us review some metrics to determine whether quantum computing is good or bad.
Limitations
1. Algorithm formulation
Developing quantum algorithms requires a deep understanding of quantum mechanics. The algorithms need to be of utmost precision and efficiency to leverage qubit properties. And it is challenging due to the non-intuitive behavior of quantum systems.
2. Hardware
The existing quantum computer sizes are very limited and fragile, and developing large ones is still a challenge to engineers, as qubits are vulnerable to losing their quantum states.
3. Cost
Building and maintaining quantum computers is expensive.
4. You need extremely low temperatures
Operating quantum computers requires extremely low temperatures, almost zero or in the minus. Maintaining the temperature is crucial to prevent decoherence.
5. Ethical concerns in quantum computing
It challenges existing cryptographic systems that secure digital communications and data storage. Algorithms like Shor’s can factor large prime numbers, and they can affect encryption methods like RSA and ECC.
6. Interoperability
There is less standardized role of this computing, which can lead to difficulty in comparing and combining various quantum computers.
Benefits
1. Speed
Quantum computing’s important pillar is dealing with complexity speed. When dealing with larger numbers, they are incredibly fast.
2. Parallelism
This is the reason behind speed; unlike classical computers, quantum computing processes many calculations at once, which solves problems much quicker.
3. Superior data handling
Quantum computers store data in qubits, which means in multiple states at once, and this makes them highly efficient for storing and processing. It is of great use in fields of AI, Big Data analytics, and machine learning.
4. Supporting new technological frontiers
These machines help us dig things beyond our reach. Researchers and engineers are leveraging quantum computing to explore science, drug discovery, AI, and quantum communication.
5. Evolving Google searches
Due to its capability of processing huge amounts of data, quant algorithms provide improved search engine performance and accurate and relevant search engine results.
6. Cryptography
One of the quantum computing challenges is also its strength, as these computers can crack the advanced encryption algorithms. They also offer fresh possibilities for better authorized and secure private communication.
Real World Applications of Quantum Computing
This advanced computer science has opened horizons for various untapped areas and the discovery of things far beyond ordinary life. Let’s explore some of its various applications.
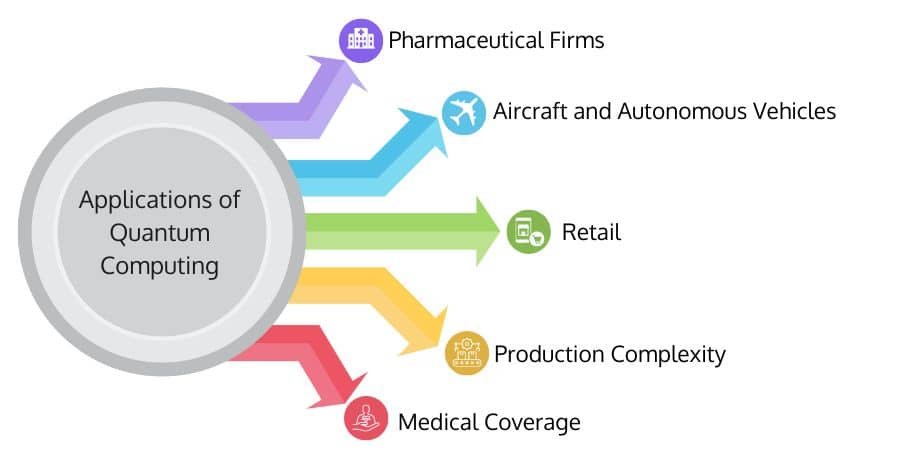
Drug Discovery
With the help of quantum computing, it is possible for researchers to get a precise understanding of how potential drugs behave with complex biological molecules in our body. This helps researchers to make drug discovery faster and select suitable candidates earlier. Impacting worldwide healthcare positively.
Fundamental Research in Physics
Though the technology is not perfect, it is significant in various fields and experiments. Today, we use GPS, MRI scans and silicon chips that have grown from the seeds of quantum computing. Recently, Google’s AI teams studied physics topics such as gravity, molecules, light particles, and new states of matter using quantum processors.
Chemistry
Ammonia alone contributes to 2-3% of global greenhouse gas emissions, and it is one of the most commonly used industrial chemicals. But this can be curbed with quantum computers being used for critical chemical processes, to stimulate better chemical reactions. Treat the chemical process in a way that is efficient and with low emissions.
Related: Inside Doxbin: The Dark Web’s Repository & Its Latest Implications
Quantum Computing FAQs
What is Schrödinger’s cat in quantum computing?
Schrödinger’s cat was an imaginary experiment conducted by the Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger. He thought, “What if I trap a cat in a closed box with an object that has 50% chances of killing it in the next hour?” According to common sense, either the cat will be dead or alive.
But Schrödinger points out that according to quantum physics, the cat is half dead & half alive at the instant before the box is opened. A quantum object can exist in two different states. This story is generally used to explain the superposition rule.
What are the main components of quantum computing?
The main components of quantum computing are:
- Qubits, which is the base and unit of information.
- Quantum gates that change the quantum states of qubits, and they control and handle superposition and entanglement principles.
- Quantum processors or QPU are the living space of qubits, and they need extreme isolation to keep them safe from noise.
- Control electronics
- Cryogenic system
- Classic computers
Final Word
Learning this rapidly growing technology is going to be exciting for you. The phenomena behind quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, make you question the obvious. Quantum physics gives you a whole different dimension of the universe and how it is being used to solve the most complex problems much faster and accurately than classical systems. There are advantages and disadvantages of quantum computing in its real-world applications discussed above. But it’s undeniable that quantum computing is exploring solutions and paving possibilities we can hardly imagine.
Keep reading! Keep learning!