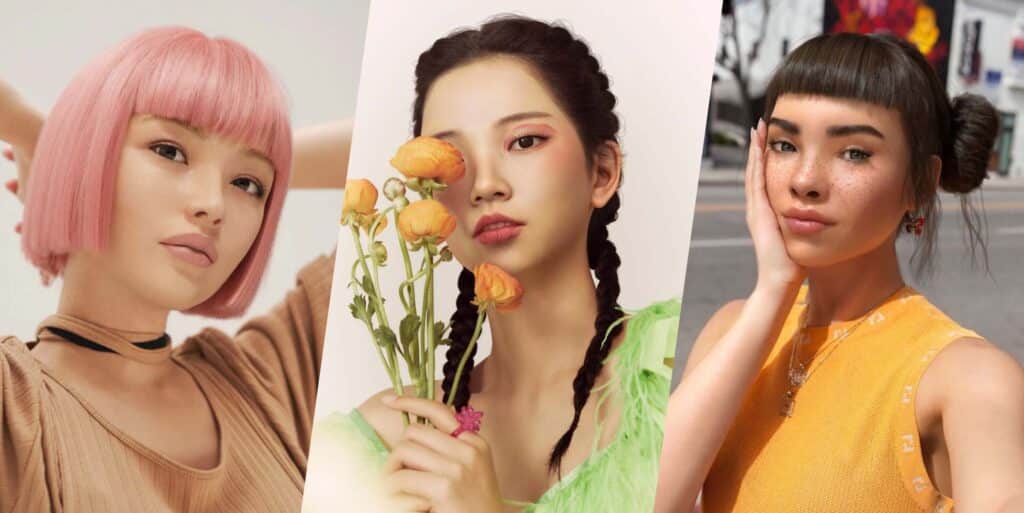
Why do we follow someone online, especially an influential personality on social media? It’s very simple; we feel inspired by them, we resonate and relate with them. It’s about the human connection we built with them through their art, skills, and stories. Imagine stumbling upon an influencer on Instagram, and you start admiring them and connecting with them, even spending on things, by being influenced. And then one day you realise they don’t exist in real life, the person you’re seeing in those picture-perfect posts is not made of flesh and blood but is generated by codes, pixels, and computer programming. Yes, they are called ‘virtual influencers’, unreal and non-existing human lookalikes which brands hire to sell you real things. Virtual influencers like Mia Zelu, who has been making headlines recently, are a prime example of it.
In this blog, we will not only uncover what AI-generated influencers are but will also dive deep into their history and some serious aspects like legalities, psychology, SEO, and the global angle around this technology of virtual influencers.
What are Virtual Influencers & Is Mia Zelu Real?

Virtual influencers are manmade digital personalities brought in to behave like real social media icons. They do not have any real-life existence, but they have a social media presence and can post images, videos, stories, and even engage with followers and collaborate with brands and become brand ambassadors.
How are they built?
These fictional personalities are created by the amalgamation of AI-generated imagery, 3D modeling, and computer graphics (CGI). Deep learning techniques and tools like Stable Diffusion, MidJourney, or Blender are used to make these human-like hyper-realistic visuals.
Without Their Existence, Who Decides What They Will Look Like?
The design team decides everything from appearance to style, and even the backstory of the character. Once designed, the character remains consistent, the face, vibe, and basic features. Just as your Marvel characters or cartoon characters stay the same.
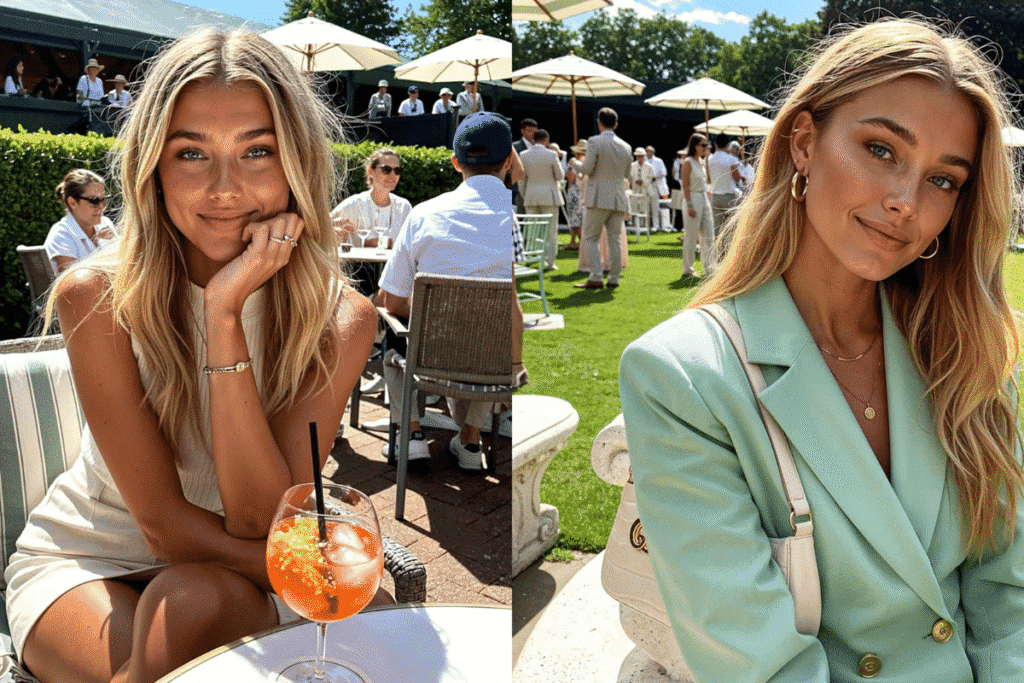
Example: Who is Mia Zelu?
Mia Zelu is not a real human but a virtual influencer who gained notable popularity in July 2025 with her Instagram post at Wimbledon. Despite a clear mention about her being an ‘AI influencer’ on her Instagram profile bio, people still thought her to be a real person and were attracted to her the same way. Her post gained nearly 50k likes, making headlines around the authenticity of the online personalities. Though she is not the first AI-generated influencer, the history of the same dates back to the 80s. I will tell you more about it going ahead.
Why are Brands Inclining Towards Virtual Influencers?
In 2023, China’s influencer marketing sector already crossed the $21 billion mark, and the industry is constantly booming with digital marketing innovations. Though the majority of brands haven’t collaborated with virtual influencers, over 60% brands have introduced them into their ad campaigns, displaying a growing virtual influencer marketing trend.
A few key reasons brands prefer virtual influencers:
1. Consistent Brand Representation & 24/7 Availability
These virtual personas can post content anytime, anywhere, with no breaks or issues in the schedules.
2. No Scandals
Since they are not real humans, there is no risk of any personal controversies or conflicts that can harm the brand image.
3. Worldwide Reach
They can be crafted to relate across cultures and markets.
4. Easy Adjustments
The appearance, personality, and narrative can be easily customized in an instant as per requirements.
5. High Predictability & Digitally Literate Image
As model content and behavior, each and everything is fully controlled; it’s easy to determine campaign results and scalability. Also, virtual influencers portray brands and businesses as innovative, creative, and thinking ahead.
6. Virality & Data-Backed Marketing
These frenzied and almost unrealistic AI images are attention pullers and curiosity sparkers, igniting media coverage. Moreover, they can be highly tested on visuals, captions, and styles to gain maximum traffic and engagement.
Also Read: Top 5 AI Trends To Look Out For In 2026
Laws Around Virtual Influencer Technology
What if the virtual influencer resembles any real human?

This virtual influencer marketing is highly prone to violation of the right to privacy and publicity. The U.S. Right of Publicity protects a well-known image, voice, or likeness from being used for nonconsensual commercial gains. A well-known 1992 White vs Samsung Electronics is a prime example of this legal implication.
How is it allowed?
Brands can freely advertise using cartoons, mascots like Amul girl, Vodafone’s Zoo Zoo. Therefore, virtual influencers are also just advanced current-age digital mascots with more realistic approaches. Though companies have been bound to maintain transparency with the consumers.
Advertising & FTC rules
Virtual influencers have been marked as regulated endorsers by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) since 2023. Their non-existence must be transparent, and brands must disclose that the personality used is non-existent. There are fines and legal penalties for misleading consumers that a fake influencer has genuinely used the product or service.
Training Data & Copyright
AI training data is another vulnerability to the appearance of these virtual influencers; if they are made or trained on copyrighted photos or depict a real model without consent, brands can end up being sued for copyright infringement. These virtual marketing sites sit in the legal gray area, with cases already rising around Gen-AI & IP rights.
Psychological & Social Impacts of Virtual Influencers
Beyond the boundaries of legal, technical, and business matters, virtual influencers are becoming questionable in terms of their psychological and social effects. They subconsciously give fire to unrealistic beauty & lifestyle expectations and standards. They are designed to be flawless, picture-perfect, and always up to date with trends. According to a stat by Dove, 90% of girls said they feel less beautiful in front of at least one social media account they follow.
These AI characteristics never gain weight, fumble, or age, and this disturbs the line between reality and fiction, which is a cause of concern for authenticity and mental health.
Future & Global Impact
Virtual influencers are on a run for global domination in the marketing and influencer sector. China’s virtual human market was worth $960 million in 2021 and is expected to hit $42 billion by 2023. Brands are adopting digital personalities worldwide, not just for their appearance but also for their customer service and media traction.
Top AI Instagram Influencers
| Sr. No. | Name | Quality Audience | Number of Followers | ER | Country | Operator |
| 1 | Lilmiquela | 1.1M | 1.7M | 1.97% | United States | Brud.fui |
| 2 | Noonoouri | 230K | 331K | 2.39% | France | IMGMODELS |
| 3 | Imma.gram | 128K | 159K | 3.46% | Japan | aww.tokyo |
| 4 | Shudu.gram | 121K | 192K | 5.39% | England | TheDiigitals |
| 5 | Bermudaisbae | 107K | 180K | 4.92% | United States | Brud.fui |
| 6 | Blawko22 | 82.4K | 145K | 3.74% | United States | Brud.fui |
| 7 | Itsbinxie | 79.5K | 103K | 5.44% | United States | Neon Evolution |
| 8 | Guggimon | 61.7K | 91.9K | 5.21% | United States | Superplastic |
| 9 | Cadeharper | 48.2K | 93.3K | 7.46% | United States | Sparkcgi |
| 10 | Janky | 43.4K | 68.6K | 7.96% | United States | Superplastic |
FAQs
1. Who was the first virtual influencer?
Lynn Minmay (1982-1984) in Japan acted like a virtual idol in an anime. But Kyoto Date (1995) was the first realistic CGI attempt pop idol marketed as a real person. Then came the hyper-realistic influencer on social media, very similar to a human influencer; she was Lil Miquela (2016).
2. Will these AI-generated characters replace real brand ambassadors, news anchors, or even politicians?
There is a possibility that it might happen with ongoing tech advancements, but there will always be concerns for privacy, ethics, trust, and accountability.
3. Are virtual influencers real people?
No, they are non-existent in real life. They are created and managed by studios, companies, or creators for commercial purposes.
4. How to differentiate between a real and a virtual influencer?
Firstly, check their profile bio to see if they mentioned themselves as AI-created, as it’s a mandate. Next, you can look for unrealistic backgrounds and overtly perfect images, also spot brand partnerships and reverse image-checks can confirm authenticity too.
Final Word
These AI-generated influencers are no longer a secret; they are drastically transforming market trends and how brands, audiences, and society interact online. They have their own pros and cons, and being flawless is one of its major root causes of several flaws. This upcoming technology and changing dynamics between humans and artificial intelligence are a challenging phase to draw a line of safety, ethics, and societal norms between virtuality and reality.
Related Read: Try Google’s Nano Banana: Best Ways to Use Nano Banana AI
Also Read: Top Programming Languages For Artificial Intelligence (AI) Apps