The average data breach cost of the world in 2025 is $4.4 million, as per IBM’s Cost of Data Breach Report 2025. Great security in your IT organization does not only mean time-to-time patch management. It goes a step beyond that! When you are in charge of a huge amount of data, experts always suggest regular vulnerability remediation.
Ponemon’s Cost and Consequences of Gaps in Vulnerability Response report states that 39% of cyberattack victims knew about a vulnerability before an attack, but did nothing to fix it. Many might find the definitions of vulnerability remediation and patch management confusing, but I will try to clear them as simply as possible.
Not only that, but in this blog, we will also learn about the process of vulnerability remediation, its scope, key elements, the process itself, why it is needed, best practices, the differences between vulnerability remediation and patch management, and other important areas.
What is Vulnerability Remediation? It’s Scope
Vulnerability remediation is often confused with patch management, but their definitions are completely different. Vulnerability remediation is the procedure of identifying, correcting, and patching vulnerabilities in a network or a system. Tech professionals literally play the game of ‘hide-and-seek’ in this case. They identify the hidden vulnerabilities using several methods. Once detected, they move on to fix these issues before any exploitation can take place.
The scope of vulnerability remediation covers every digital asset, including servers, user accounts, databases, software applications, and many others. Any asset that can be exploited by external agents with unauthorized access must be considered for remediation.
Effective Elements of Vulnerability Remediation
Vulnerability remediation consists of some key elements that you must consider:
1. The first step is vulnerability identification.
You cannot fix issues that you do not know exist. That’s why it is one of the vital steps. Tech teams use penetration testing and vulnerability scanners to detect weak areas in the system.
2. The second step is prioritizing.
Once you are done identifying, now comes prioritizing the vulnerabilities. It is not possible to fix them all simultaneously, so professionals identify the ones that need urgent fixing. In this step, you need to consider its severity, impact, and whether it can be easily exploited or not.
3. The third step is remediation.
Now you must patch these vulnerabilities using various methods, like updating, adjusting the configuration, or employing new security measures. You must consider the nature of the vulnerability before taking any action.
4. The fourth and final step is verification.
Once the patching is done, you must check the system for its success or any new issues. You can do this by re-scanning the system or checking log files to confirm if the strategy has worked or not.
Required Tools
To remediate vulnerabilities successfully, you need to use a set of specialized tools that automatically detect, prioritize, and eliminate across various technological areas.
Here is a list of some essential tools when it comes to vulnerability remediation.
- Vulnerability scanners to identify weaknesses in the system.
- Remediation orchestration platforms to automate and synchronize changes in configuration, patching, and risk mitigation measures.
- Integrated management suites to streamline workflow by putting together detection, analysis, prioritization, and remediation in a single console.
- GitOps security tools, specialized cloud, and containers for live prioritization for cloud-based and developer-centric systems.
Some Examples:
- Tenable.io for vulnerability management and remediation.
- Qualys VMDR for vulnerability detection and response.
- Rapid7 InsightVM for real-time risk analysis and tracking remediation.
- SentinelOne for automated remediation.
- Automox for automated patching and remediation.
- Wiz for vulnerability management in cloud-first environments.
- OpenVAS for scanning, detecting, and reporting.
Process of Vulnerability Remediation
As you might have already learnt briefly, the overall process of vulnerability remediation includes detection, prioritization, remediation, and constant monitoring. Let’s go through them one by one.
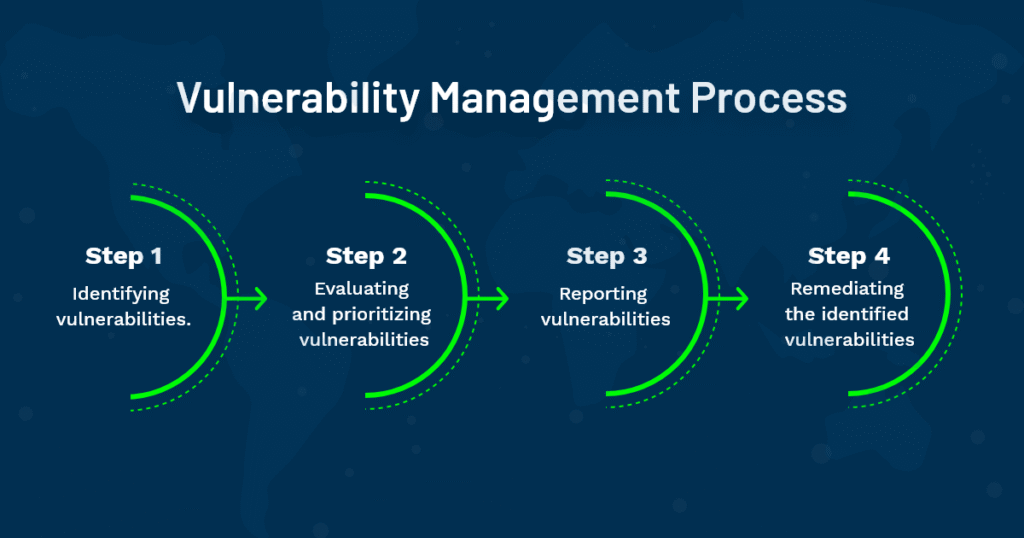
- Vulnerability Identification: To protect your digital assets, it is important to detect vulnerabilities. For detection, organizations can use specialized tools like penetration testing and vulnerability scanners. These scanners detect weak points in the system. A more proactive way is to use penetration testing to test the system’s strength. They do so by trying to breach it and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Resolution Prioritization: Once detection is done, you must prioritize the vulnerabilities according to their severity. Those that pose the maximum risks, can cause major damage, and/ or are easily exploitable, should top your list. This step also allows efficient use of resources.
- Vulnerabilities Remediation: In this step, you address the vulnerabilities. It requires you to take action to secure your digital environment. These actions can be updating software, adjusting configurations, or introducing new security measures.
- Constant Monitoring: With continuous monitoring, two important things are taken care of. First is the detection of new vulnerabilities, and second is to ensure the prior fixes are constantly effective.
Each of the vulnerability remediation process steps is crucial to maintaining the security and hygiene of your digital environment. Compromising any one of them can lead to a massive disaster.
Vulnerability Remediation & Vulnerability Management: Difference & Roles in Cybersecurity
For many, both the terms vulnerability remediation and vulnerability management might sound similar. But professionals never make the mistake of using it interchangeably.
Here are the differences between the two terms:
The process of detecting system vulnerabilities, prioritizing them accordingly, and fixing them to prevent any upcoming cybersecurity threat is vulnerability remediation. Imagine a class of students, as a teacher, you identify the weaker ones and try to provide them with extra classes for remediation.
On the other hand, vulnerability management is the larger, more strategic process. Besides remediation, it includes strategic development for continuous monitoring, analysis, and reporting of vulnerabilities.
In this case, being the teacher, you make strategic decisions to prevent students from becoming weak in the long run.
Their roles in the cybersecurity arena:
When it comes to the cybersecurity of your organization, vulnerability remediation is the frontline defense system. It acts quickly to fix all known vulnerabilities, improving system performance and reducing external risks.
Vulnerability management is strategic remediation for the long haul. It checks the overall security posture, identifies vulnerability trends, and plans resource allocation. It ensures that all efforts are done timely, effectively, and in alignment with the organization’s long-term cybersecurity goals.
Why Do Organizations Need Vulnerability Remediation?
When it comes to an organization’s cybersecurity, vulnerability remediation is important. Let’s understand why systemic vulnerability remediation is so vital today.
To Minimize Security Risks
A systematic approach to vulnerability remediation is needed to effectively reduce cybersecurity threats. By applying vulnerability remediation best practices, organizations must detect, prioritize, and fix security loopholes.
To Improve Efficiency
Having a vulnerability remediation system improves efficiency within organizations. Having a clear roadmap ensures your tech team saves time on self-detecting security gaps. Instead, the response time becomes faster, and resources get utilized effectively.
To Guarantee Compliance
A formal vulnerability remediation strategy ensures that the organization complies with industry regulations. You also have the needed documents in case you need to prove the compliance and to uphold your company’s reputation.
To Grow Responsiveness
A systematic process also oversees the response time of your team to new vulnerabilities and improves it. When you have a distinct roadmap, there’s no time wasted on deciding the next steps. You can step in quickly, fix security gaps to eliminate potential security breaches.
Difference between Vulnerability Remediation and Patch Management
Though closely related to each other, vulnerability remediation and patch management serve different purposes in cybersecurity. In this case, vulnerability remediation is the broader prospect, and patch management is just a small part of it.
| Feature | Patch Management | Vulnerability Remediation |
| Coverage | Identified software issues | Overall security issues |
| Remediation Process | By applying patches from vendors | By performing software updates, configuration changes, policy updates, etc. |
| Frequency | As per the vendor schedule | Continuous |
| Tools | Platforms for patch deployment | Risk engines, scanners |
| Examples | Windows update | Imposing MFA on exposed databases |
Role of AI in Vulnerability Remediation
At the beginning, we got to know the massive cost of global data breaches in 2025. But, do you know some good news? The cost of 4.4 million dollars is 9% less than last year’s (2024). Simply because the threats were identified and contained within time. Also, organizations internationally saved $1.9M by implementing AI in security in comparison to organizations that did not use these AI initiatives.
Now, let’s understand the role of AI in vulnerability remediation in modern organizations.
- It enables real-time identification and analysis of security gaps. AI continuously monitors system logs, traffic, and code repositories. Also, ML algorithms process huge data streams to decrease dwell time and identify zero-day vulnerabilities faster.
- AI gives standard vulnerability scoring processes a huge makeover by considering real-world business impact, threat intelligence, and exploit likelihood.
- Artificial intelligence can also activate remediation processes, like patch deployments, policy updates, etc., automatically.
- Based on evolving threats and system operations, AI enables an adaptive response mechanism to adjust remediation processes dynamically.
- Gen AI models can elevate collaboration and quicken resolution by giving end-to-end instructions to IT teams and developers.
- AI platforms also coordinate remediation efforts across an organization’s overall security infrastructure, enabling a multi-layered defense mechanism.
Best Practices of Vulnerability Remediation
To improve your company’s cybersecurity infrastructure, you must implement a well-structured vulnerability remediation approach. This includes,

- Just like a 24/7 security system, implementing continuous monitoring software helps to identify threats in real-time and prevents cyber criminals from exploiting them.
- Another important step is to prioritize vulnerabilities. To enhance resource optimization, always consider the most dangerous vulnerabilities first.
- To successfully remediate vulnerabilities, maintain documented security policies. Using this method reduces guesswork, improves team productivity, and provides a path of clarity.
- Understanding your system, its operation, components, and connections, quickens both the detection of vulnerabilities and the finding of proper solutions for them.
Conclusion
Hopefully, by now, you have a good idea of what vulnerability remediation is, what differs between vulnerability remediation, patch management, and vulnerability management. These tech terms can sound so similar, but are quite different as you have already learnt.
It’s almost 2026, and organizations today understand the importance of maintaining security standards. Especially with AI, many global companies have seen a surge in sophisticated cyber threats and breaches, claiming millions of dollars in losses. The other side of the coin is using AI in vulnerability remediation to detect these system loopholes and manage them accordingly, saving millions of dollars in return.
So, decide quickly which side you want to be on, gaining or losing, with the power of AI?







